Telecommunication ~ Different types of computer cabling
The cable is the medium through which information generally passes from one network device to another. There are several types of cable commonly used with local area networks..
In some cases, a network will use a single type of cable, other networks will use a variety of cable types. The type of cable chosen for a network is related to the topology, protocol and size of the network. Understanding the characteristics of the different cable types and their relationship to other aspects of a network is necessary to develop a successful network.
The following sections describe the types of cable used in networks.
- Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable
-Shielded twisted pair (STP) cable
-Coaxial cable
-Optical fiber
Twisted pair cable:
There are two types of twisted pair cable: shielded and unshielded. Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) is the most popular and is generally the best option for school networks.
Unshielded twisted pair cable (UTP)
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) is a ubiquitous type of copper cabling used in telephone wiring and local area networks (LANs). There are five types of UTP cable (identified by the CAT prefix), each supporting a different amount of bandwidth.
The quality of UTP can vary from telephone wire to very high speed cable. The cable has four pairs of wires inside the jacket. Each pair is twisted with a different number of twists per inch to help reduce crosstalk and interference from adjacent pairs and other electrical devices. The tighter the twist, the higher the transmission rate supported.
Twisted pair cable connector (RJ45)
The standard connector for unshielded twisted pair cabling is the RJ-45 connector. It is a plastic connector that looks like a large telephone-type connector. RJ stands for Registered Jack, which implies that the connector conforms to a standard borrowed from the telephone industry. This standard designates which wire goes with each pin inside the connector.
Shielded twisted pair cable (STP)
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) cable was originally designed by IBM for token ring networks consisting of two individual wires covered with a shielding foil, which prevents electromagnetic interference, allowing faster data transport.
STP is similar to unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable; however, it contains an additional aluminum jacket or copper braid sheath to help protect the cable signals from interference. STP cables are more expensive than UTP cables, but have the advantage of being able to support higher transmission rates over longer distances.
Although UTP cable is the least expensive, it can be subject to radio frequency and electrical interference. If you need to place the cable in highly disturbed environments, or in extremely sensitive environments, STP may be the solution. Shielded (STP) cables can also help extend the maximum cable distance.
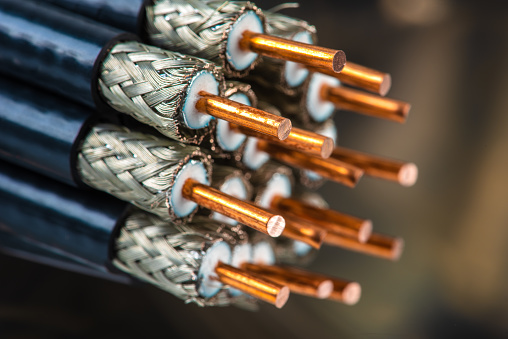
Coaxial cable:
Coaxial cable is a type of specially constructed copper cable with a metal shield and other components designed to block signal interference. It is primarily used by television companies to connect their satellite dishes to customers' homes and businesses. It is also sometimes used by telephone companies to connect telephone exchanges to telephone poles near their customers. Some homes also use coaxial cable, but its widespread use as a means of Ethernet connectivity in businesses and data centers has been replaced by the deployment of twisted pair cabling.
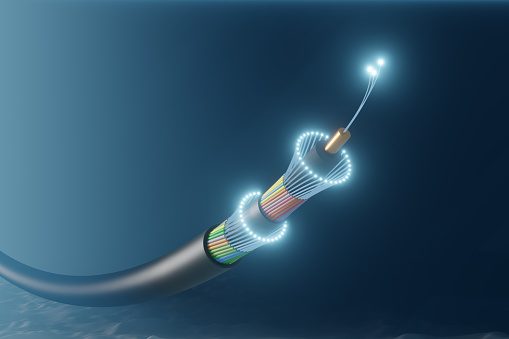
Optical fiber:
Fiber optics consist of a central glass core surrounded by several layers of protective material. It emits light rather than electronic signals, thus eliminating the problem of electrical interference. This makes it ideal for certain environments containing a lot of electrical interference. It is also built for connecting networks between buildings, because of its immunity to the effects of moisture and light.
Fiber optic cable has the ability to transmit signals over much longer distances than coaxial and twisted pairs. It also has the ability to carry information at much higher speeds. This capability expands communication possibilities to include services such as video conferencing and interactive services. The cost of fiber optic cabling is comparable to that of copper. However, it is more difficult to install and modify. 10BaseF refers to the specifications for optical fibers carrying Ethernet signals.
There are two common types of fiber optics - single-mode and multi-mode. The multimode cable has a larger diameter; however, both cables provide high bandwidth at high speeds. Single mode can provide more distance, but is more expensive.
THANK YOU for reading
You Tech 56


Comments
Post a Comment